What is Thin Wall Injection Moulding?
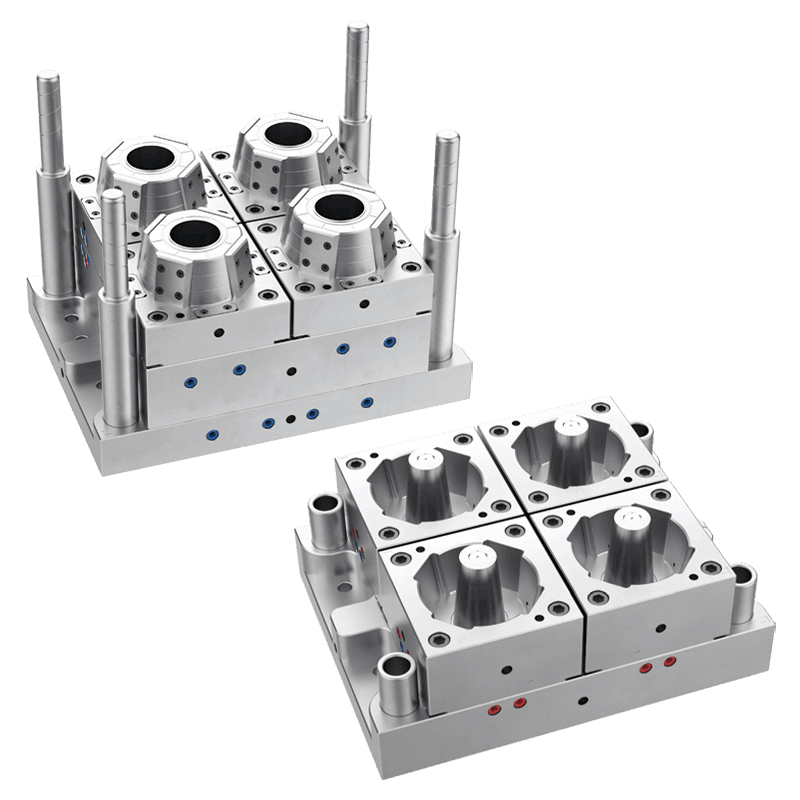
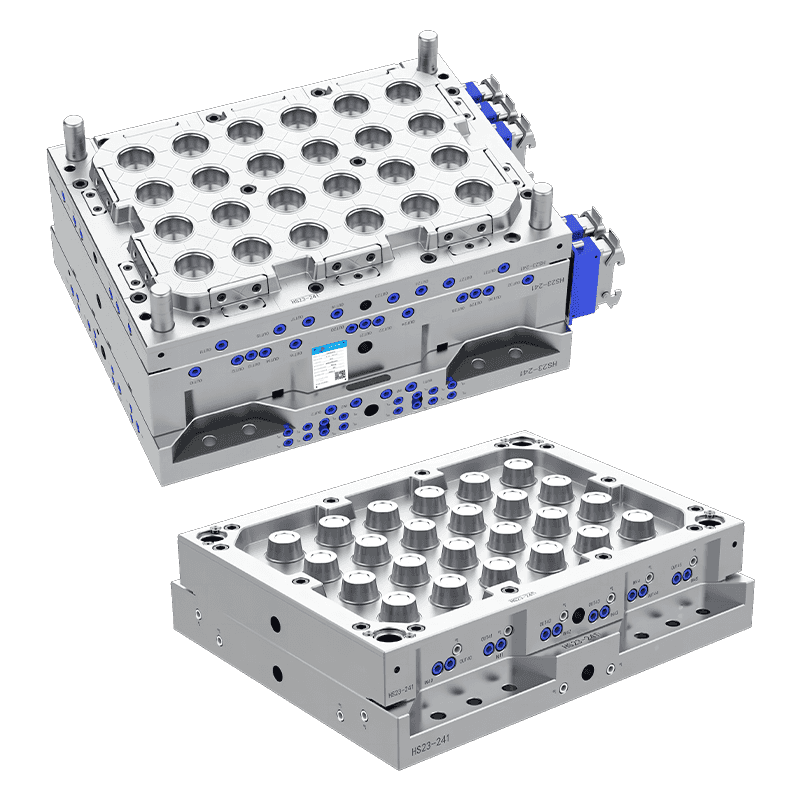
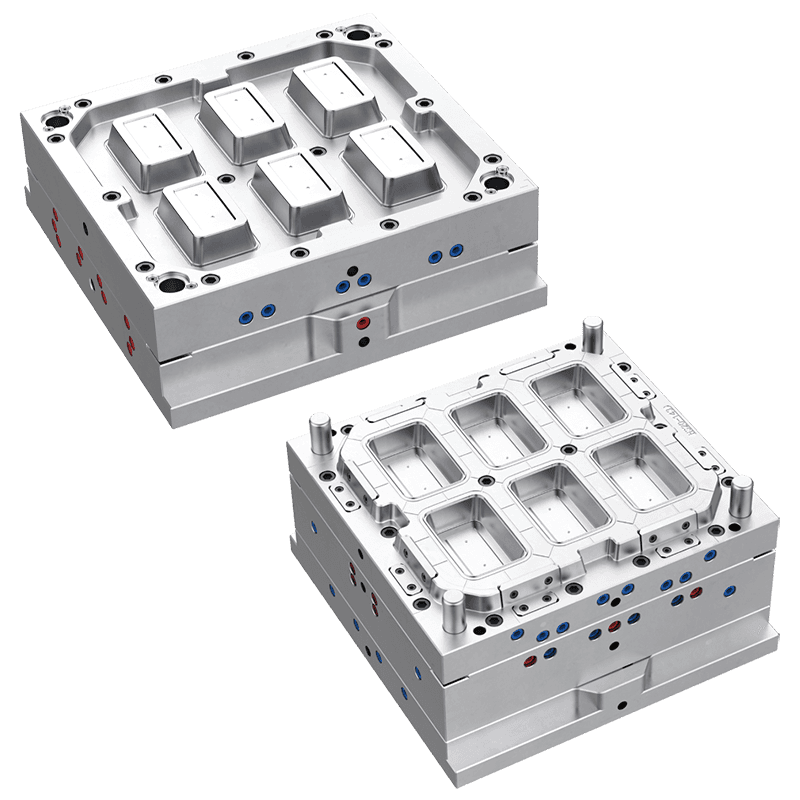
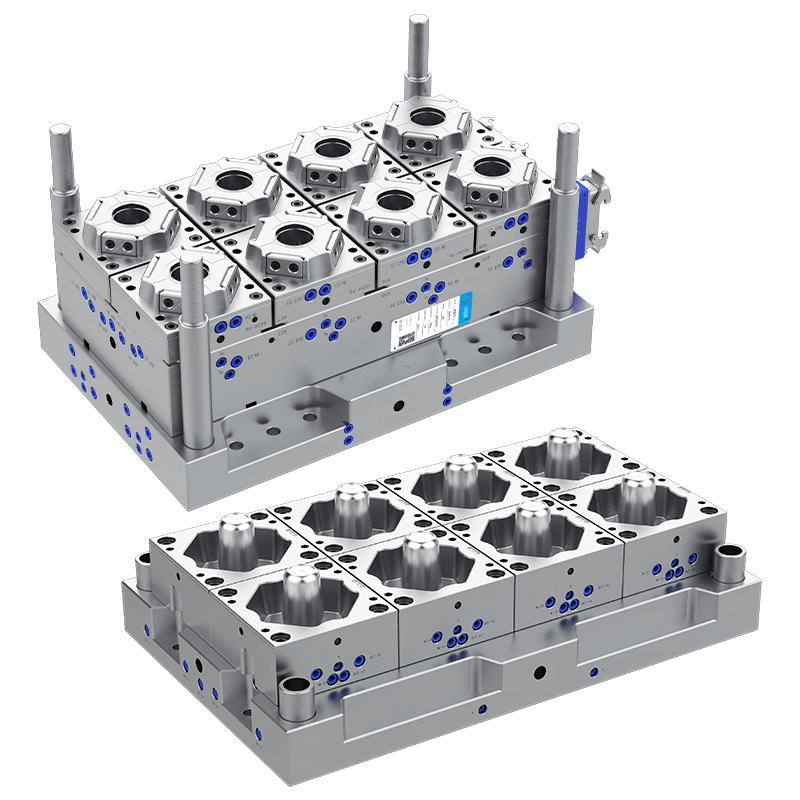
Thin wall injection moulding is a specialized process in plastic manufacturing that produces parts with thin and uniform wall thickness. This technique is used to create lightweight components with precise dimensions and consistent quality. Unlike standard injection moulding, thin wall moulding requires faster injection speeds, higher pressures, and carefully designed molds to ensure complete cavity filling without defects.
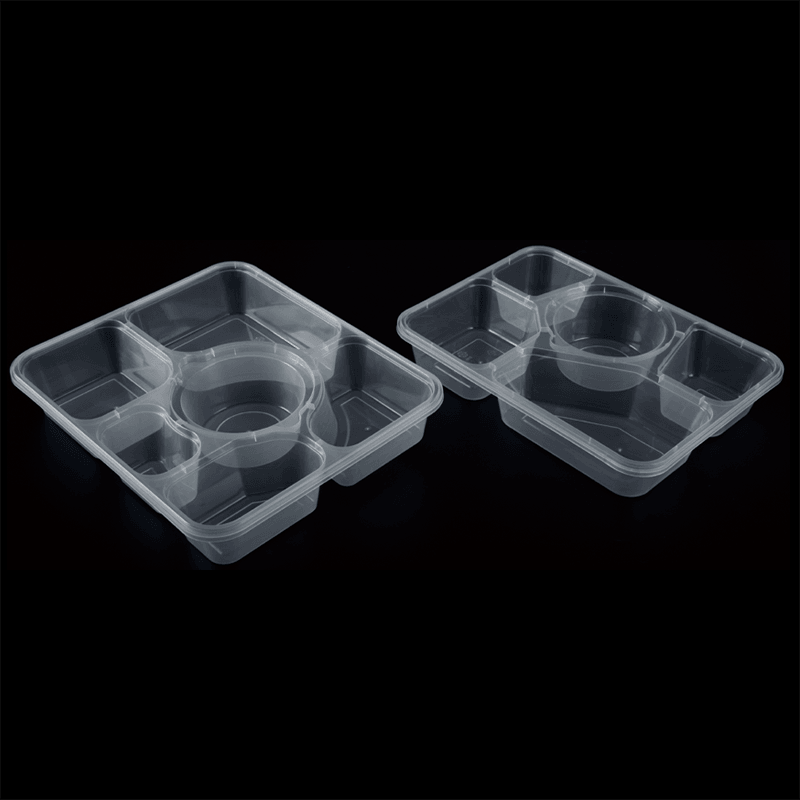

High-Speed Injection: The process involves rapidly injecting molten plastic into a mold cavity to fill thin sections before the material cools.
Precise Wall Thickness: Parts typically have walls ranging from 0.2 mm to 2 mm, requiring accurate control of flow and cooling.
Material Efficiency: Thin wall parts use less plastic, reducing material costs and overall product weight.
Mold Design Considerations: Molds must be rigid and well-cooled to withstand high pressures and maintain dimensional accuracy.
Applications: Commonly applied in packaging, electronics, automotive components, and consumer goods where lightweight, compact, and precise parts are needed.
Thin wall injection moulding allows manufacturers to produce parts that are consistent in thickness, size, and appearance, supporting both functional and aesthetic requirements. Its primary focus is efficiency in material use and maintaining high-speed production capabilities.
Why Does Thin Wall Injection Moulding Occur?
Demand for Lightweight Components
Thin wall injection moulding occurs due to the need for lightweight plastic parts. Industries such as packaging, electronics, and automotive seek materials that reduce weight while maintaining strength. Thinner walls help achieve these requirements without compromising part functionality.
Efficiency and Material Savings
Manufacturers adopt thin wall moulding to save material costs. Using less plastic per part reduces expenses in mass production. Additionally, thinner parts require less cooling time, supporting faster production cycles and higher throughput.
Technological Advancements
The development of high-speed injection machines, precise temperature control, and improved mold designs has enabled thin wall injection moulding. Modern equipment allows faster filling, better flow control, and minimal defects, which previously limited the feasibility of thin wall production.
Environmental Considerations
Reducing material usage also contributes to lower environmental impact. By using thinner sections, manufacturers can reduce plastic consumption and energy required for processing, aligning with sustainability goals.
The Process of Thin Wall Injection Moulding
Thin wall injection moulding follows a process similar to standard injection moulding but with key adaptations to handle thin-walled components.
Material Preparation: Thermoplastic pellets are dried to remove moisture and heated to a molten state. Proper drying prevents defects like voids or bubbles.
High-Speed Injection: Molten plastic is injected rapidly into the mold cavity. High injection speed is crucial to ensure the entire cavity is filled before the material begins to cool and solidify.
Pressure and Flow Control: High injection pressures are applied to force the molten plastic into thin sections. The flow rate is carefully monitored to prevent incomplete filling, flow marks, or warping.
Cooling: The mold is designed with efficient cooling channels to remove heat quickly. Rapid and uniform cooling is necessary to maintain dimensional accuracy and prevent shrinkage or deformation.
Ejection: Once the part is sufficiently cooled, it is ejected from the mold. Thin wall parts require careful ejection to avoid deformation or surface damage.
Post-Processing: Some parts may undergo trimming, inspection, or additional finishing, depending on application requirements.
Contact Us
Email: [email protected]; Or fill out the contact form below.

 English
English 中文简体
中文简体 русский
русский Español
Español Français
Français