What is a mould for plastic cups?
What is a Mould for Plastic Cups?
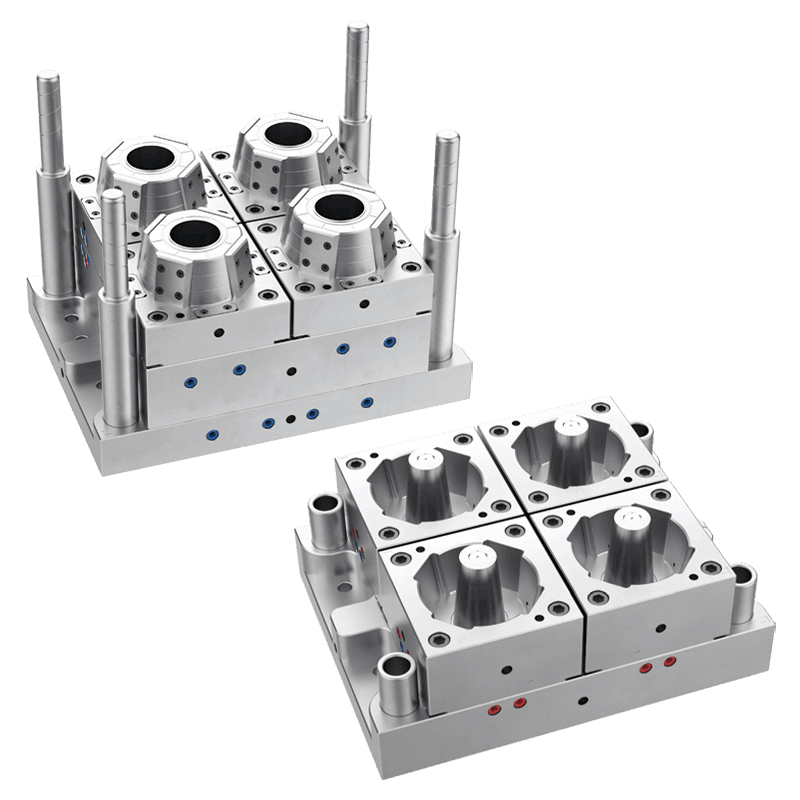
A mould for plastic cups is a tool used in the plastic manufacturing industry to shape thermoplastic materials into cup forms. The process typically involves injection molding or thermoforming, depending on the type of plastic and production requirements. In injection molding, molten plastic is injected into a mold cavity under high pressure. Once cooled and solidified, the part is ejected, forming a cup with consistent shape and size.

Plastic cup molds are usually made of steel or aluminum due to their durability and thermal conductivity. Steel molds are preferred for high-volume production because they withstand repeated cycles and maintain dimensional accuracy. Aluminum molds are lighter and often used for small-scale or prototype production.
The mold design includes multiple components, such as cavities, cores, cooling channels, and ejection systems. Cavities define the cup shape, cores maintain the internal hollow, cooling channels control temperature during solidification, and ejection systems release the finished part without damage. Proper design ensures uniform wall thickness, minimal defects, and consistent quality.
Question 2: How Are Plastic Cup Moulds Maintained?
Maintenance of a plastic cup mold is crucial for long-term performance and consistent product quality. Regular cleaning is required to remove plastic residues, dust, and debris that may accumulate on the mold surface. Lubrication of moving components such as ejector pins and slides is necessary to prevent wear and ensure smooth operation.
Routine inspections help detect early signs of wear, such as scratches, dents, or corrosion. Addressing these issues promptly can prevent defects in the molded cups, such as uneven walls, warping, or flash. Cooling channels should be checked for blockages, as improper cooling can affect dimensional accuracy.
Maintenance schedules are often determined by production volume and material type. Using proper maintenance practices extends mold life, reduces downtime, and supports consistent output, which is essential for high-volume manufacturing.
Question 3: What Types of Plastic Cup Moulds Are Common?
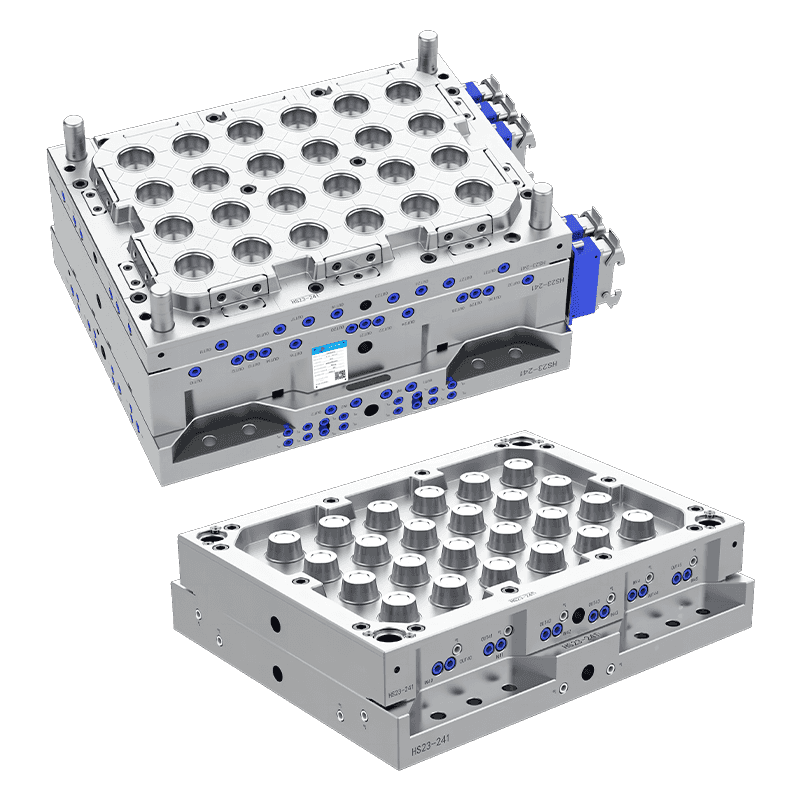
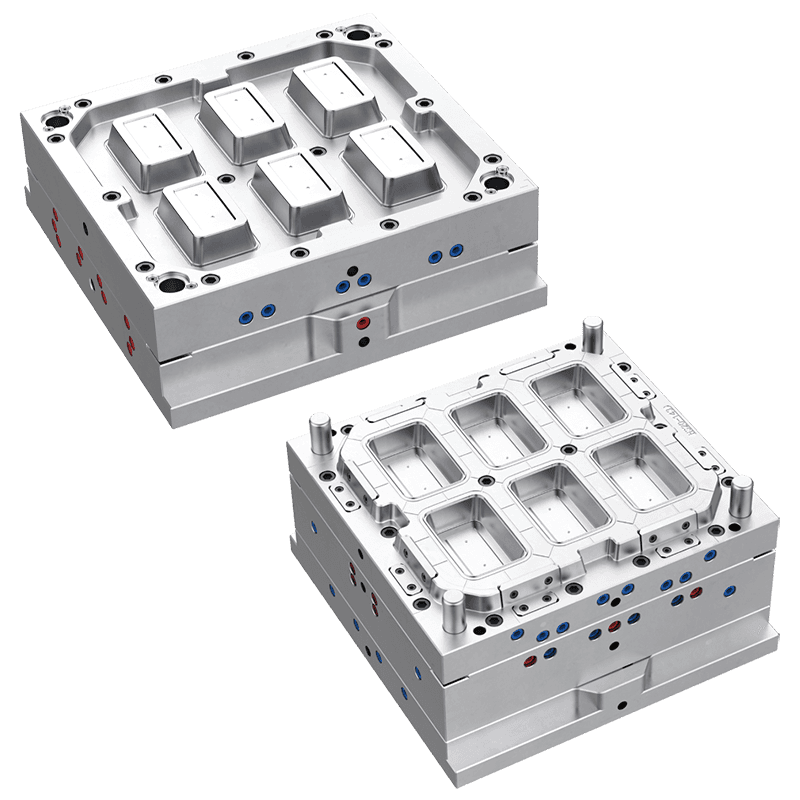
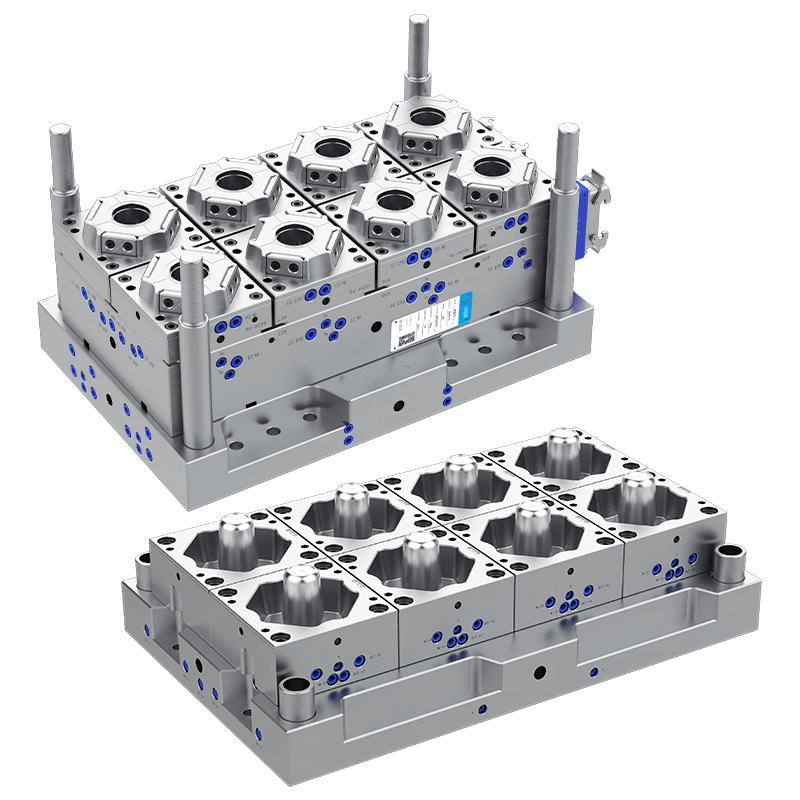
Plastic cup molds vary depending on the production method, cup design, and output requirements. Common types include:
Single-Cavity Moulds: Produce one cup per cycle, suitable for small-scale or prototype production.
Multi-Cavity Moulds: Produce multiple cups per cycle, improving efficiency for mass production.
Thermoforming Moulds: Used for forming thin plastic sheets into cups through heat and pressure.
The choice of mold type depends on production needs, material selection, and cost considerations. Multi-cavity molds are typically used in industrial settings due to higher output, while single-cavity molds are more flexible for custom or small-batch runs.
Question 4: What Factors Affect the Quality of Plastic Cup Moulds?
Several factors influence the quality of molded cups. Material selection for both the mold and the plastic is critical. High-quality steel or aluminum molds maintain shape and resist wear, while the plastic material affects flow, cooling, and final cup characteristics.
Mold design also plays a role. Proper wall thickness, cavity alignment, and cooling channel placement ensure uniformity and prevent defects. Processing parameters, such as injection speed, temperature, and pressure, must be controlled to produce consistent results.
Additionally, environmental factors, such as workshop temperature and humidity, can affect mold performance and plastic behavior. Monitoring these conditions helps maintain consistent quality. Proper maintenance and timely repairs also contribute to the long-term reliability of the molds.
Contact Us
Email: [email protected]; Or fill out the contact form below.

 English
English 中文简体
中文简体 русский
русский Español
Español Français
Français