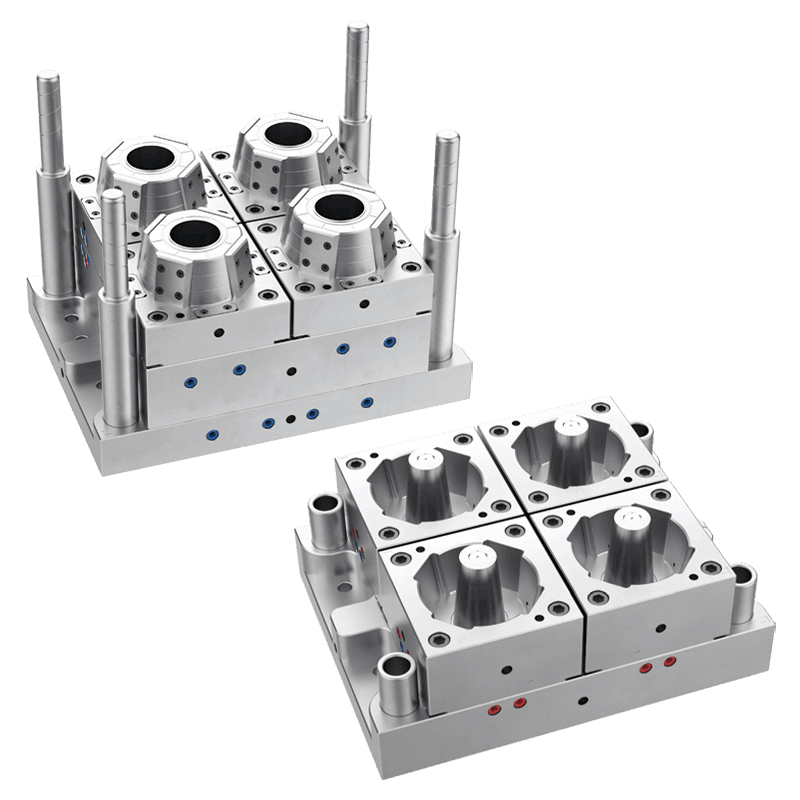
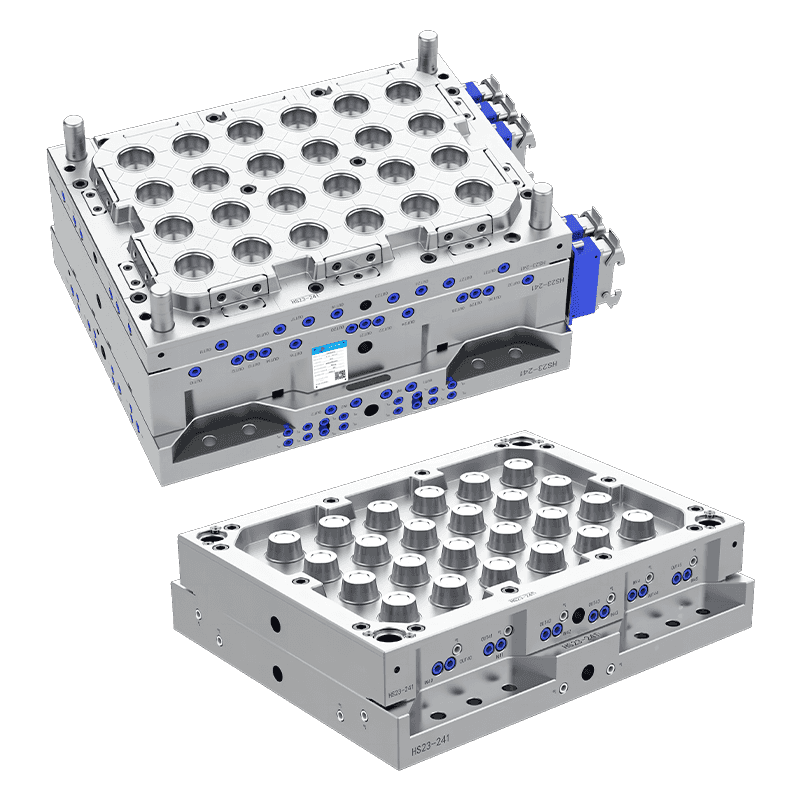
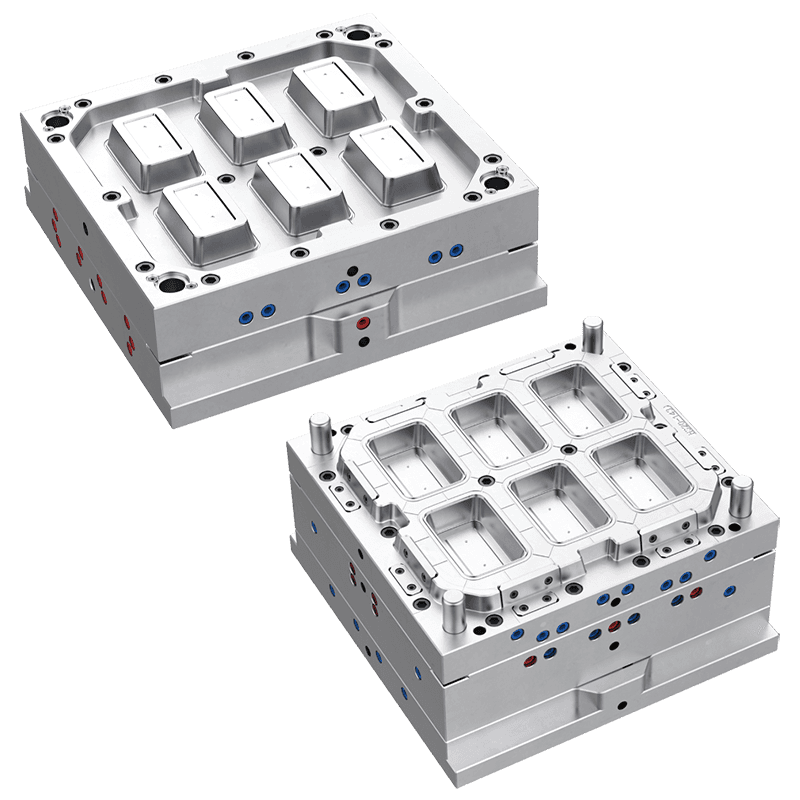
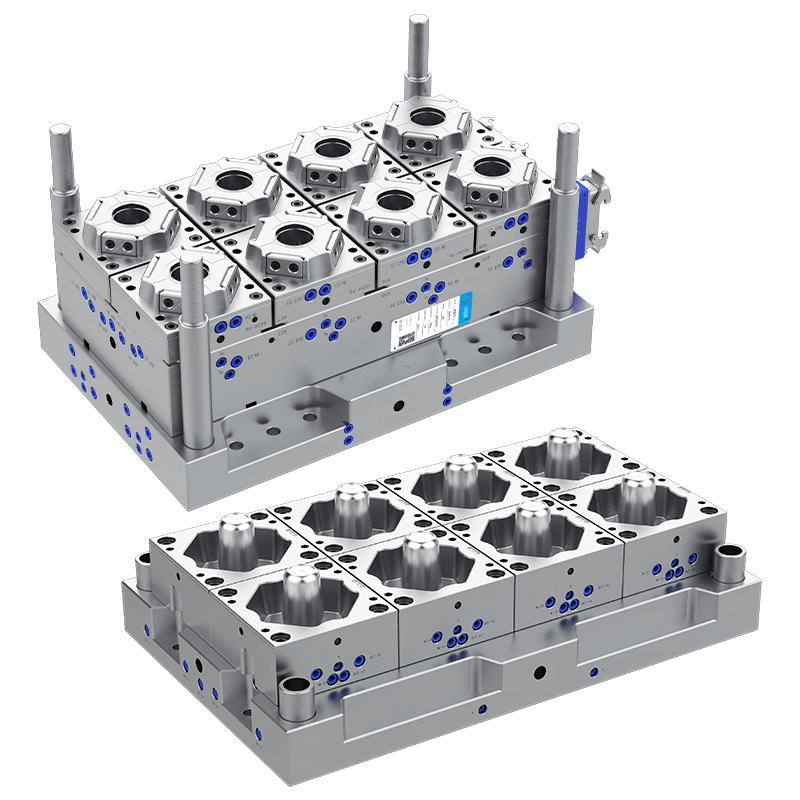
Production of Thin-Wall Food Container Molds
Thin-wall food container molds are used to manufacture lightweight, yet strong, containers made from plastic. These molds are specifically designed to create containers with thin walls, typically in the range of 0.2 to 1 millimeter in thickness, depending on the material used. The containers produced by these molds are used for various food products, including salads, sauces, soups, and ready-to-eat meals.
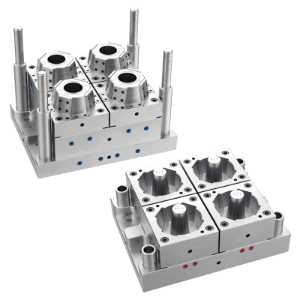
The mold design for thin-wall food containers is crucial to ensure that the containers are both structurally sound and capable of withstanding the demands of modern food packaging. A thin-wall mold must be able to handle high-speed production and meet strict hygiene standards, all while maintaining precise dimensions and durability.
Materials Used in Thin-Wall Food Container Molds
The materials selected for thin-wall food container molds must meet specific criteria, including durability, heat resistance, ease of machining, and resistance to wear and corrosion. The following are the primary materials used in the production of these molds:
1. Steel Alloys
Steel alloys are the common material used for thin-wall food container molds due to their strength, durability, and resistance to wear. These materials are selected for their ability to withstand the high pressures and temperatures associated with the injection molding process.
Hardened Tool Steel (P20, H13): P20 is one of the widely used tool steels for mold production. It provides a good balance of machinability, wear resistance, and durability. H13, another popular tool steel, is known for its high heat resistance and ability to handle high-temperature processes without losing its strength. These types of steels ensure that the mold can endure repeated cycles of high-pressure molding and still retain its structural integrity.
Stainless Steel (S136): Stainless steel is commonly used in the production of food container molds, especially when food safety and corrosion resistance are top priorities. Stainless steel molds are highly resistant to rust and degradation, making them ideal for manufacturing containers that are used to store food. S136 steel, in particular, is often chosen because of its exceptional corrosion resistance and the fact that it can withstand high pressures during injection molding.
Tool Steel with High Chromium Content: In some applications, tool steels with higher chromium content may be used to provide better wear resistance and longevity. These materials ensure that the mold performs efficiently and consistently over time.
2. Aluminum Alloys
While steel alloys are more commonly used, aluminum alloys are also a popular choice for thin-wall food container molds, particularly in low- to medium-volume production. Aluminum molds are lightweight, cost-effective, and easy to machine, making them ideal for rapid prototyping and shorter production runs.
Benefits of Aluminum: Aluminum molds provide faster cooling times, which enhances production efficiency. They are also less expensive than steel molds and can be more easily modified, which is beneficial for companies looking to experiment with different container designs. However, aluminum molds are less durable than steel, so they are generally used for lower-volume production or for testing new mold designs.
3. Beryllium Copper Alloys
Beryllium copper alloys are used in some advanced thin-wall food container molds due to their high thermal conductivity. This allows the molds to cool more rapidly, which is a critical factor when producing large quantities of containers quickly. These alloys combine the strength and hardness of copper with the corrosion resistance of beryllium, providing enhanced performance in high-speed injection molding environments.
Thermal Management: The thermal conductivity of beryllium copper helps in maintaining consistent cooling throughout the mold, which leads to improved cycle times and better consistency in the final product. These molds are typically used in high-precision molding operations where temperature control is vital.
Contact Us
Email: [email protected]; Or fill out the contact form below.

 English
English 中文简体
中文简体 русский
русский Español
Español Français
Français