How to Choose a Spoon Mold?
Spoon molds are important tools in the manufacturing of plastic, metal, or wooden spoons. They determine the shape, size, and consistency of each product and play a key role in production efficiency and quality. Selecting the right spoon mold requires understanding several factors, including material compatibility, design requirements, production capacity, and durability. The following sections answer four essential questions to guide the choice of a spoon mold.

What Material Will the Mold Produce?
The question to consider is the type of material the spoon mold is designed for. Spoon molds can be used with plastic, metal, or wood, and each material has different requirements.
For plastic spoons, the mold must withstand high temperatures and pressure during injection or compression molding. For metal spoons, die-casting molds are required, which can tolerate molten metal temperatures and provide precise shaping. Wooden spoons use carved or pressed molds, often requiring lower temperatures but high precision for carving or pressing. Choosing a mold compatible with the material ensures proper shaping, minimizes defects, and prolongs the mold's service life.
What Shape and Size Are Needed?
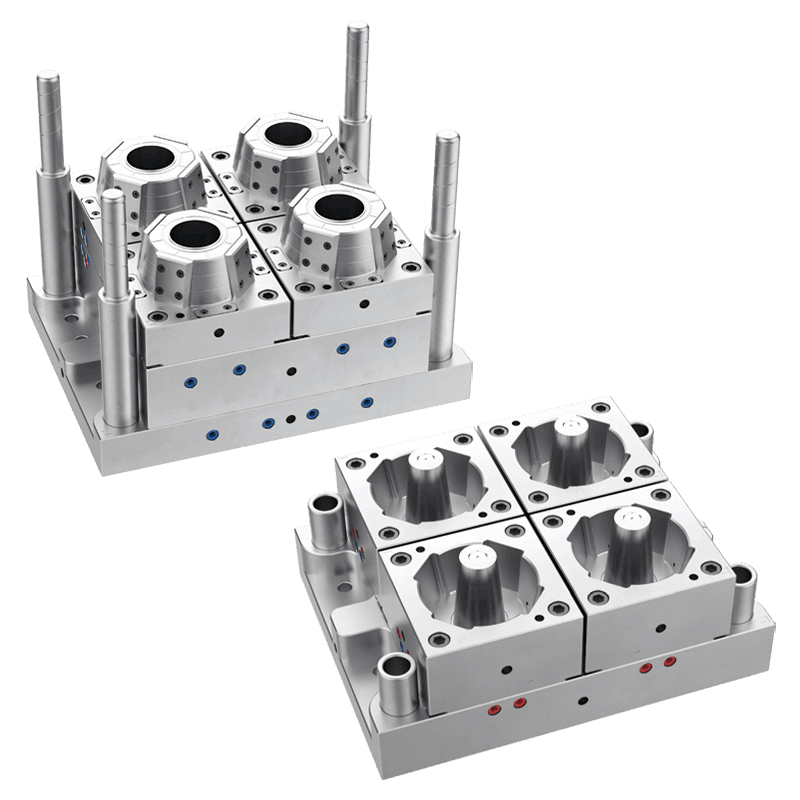
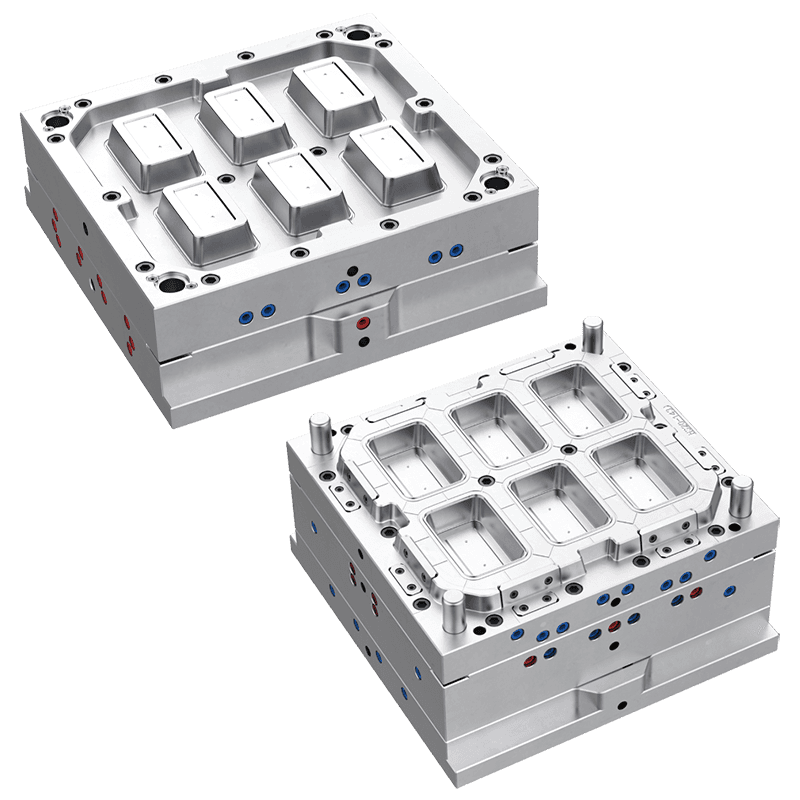
Another important consideration is the spoon's intended shape and size. Different molds allow for various spoon designs, such as teaspoons, tablespoons, dessert spoons, or specialty shapes. The mold should be selected to match the exact dimensions, handle design, and bowl depth required for the finished product.
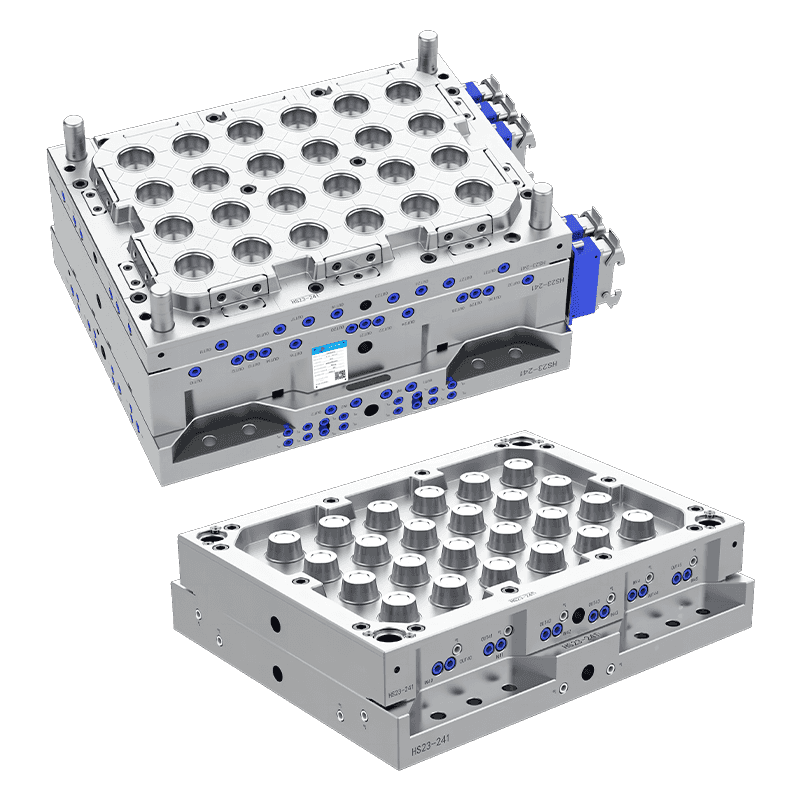
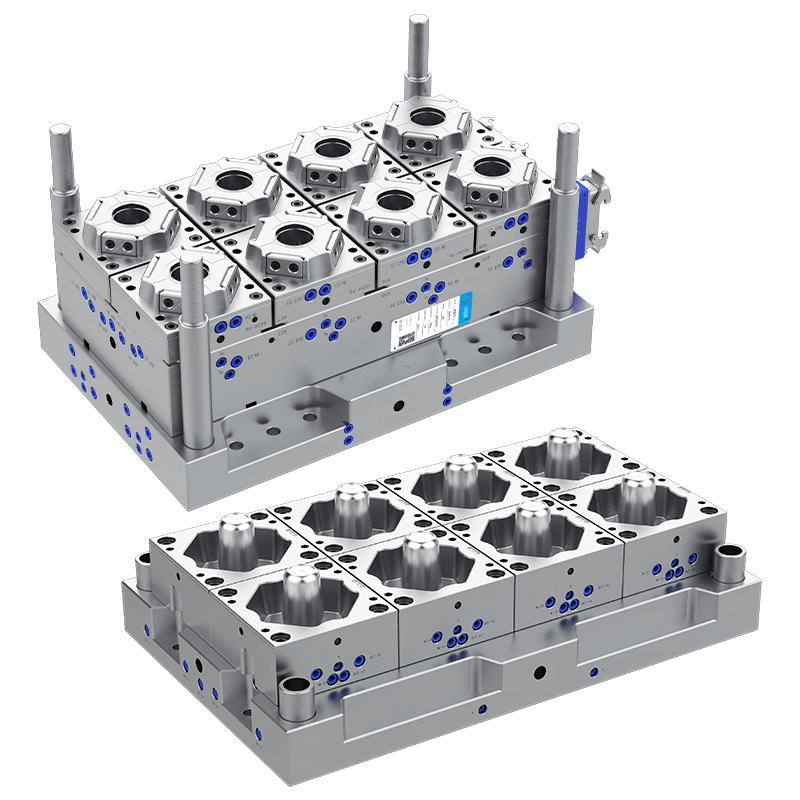
Multi-cavity molds can produce several spoons simultaneously, which is useful for large-scale production. Custom molds may also include features such as embossed logos, textured handles, or decorative patterns. Understanding the desired design and size ensures that the mold will produce spoons that meet functional and aesthetic requirements.
What Production Volume Is Required?
Production capacity is a key factor in mold selection. High-volume production requires molds that can operate continuously without frequent maintenance or wear. Multi-cavity molds, automated feeding systems, and high-precision components can improve output and efficiency.
For small or specialized batches, simpler molds with fewer cavities may be sufficient. These molds are easier to maintain and are more flexible for producing limited quantities or custom designs. Evaluating the expected production volume helps determine the type, size, and complexity of the spoon mold needed for efficient operations.
What Durability and Maintenance Are Necessary?
The durability of a spoon mold affects both production reliability and cost. Molds made from high-quality steel, aluminum, or other durable materials can withstand repeated cycles without deforming or losing precision. For metal or plastic molds, proper surface treatment and hardness are important to prevent wear from repeated heating or pressure.
Maintenance is also a consideration. Molds that are easy to clean, disassemble, and repair reduce downtime and extend operational life. Lubrication, coating, and regular inspection are necessary to maintain consistent performance. Choosing a mold with appropriate durability and maintenance features ensures long-term reliability and reduces the risk of defects in the final spoons.
Choosing a spoon mold requires careful consideration of several factors. The mold must be compatible with the material used, whether plastic, metal, or wood, to ensure proper shaping and longevity. Second, the shape and size of the spoon must match production requirements, including any decorative features or custom designs. Third, the expected production volume should guide the selection of multi-cavity or simple molds to balance efficiency and flexibility. Finally, durability and ease of maintenance are critical for long-term reliability and consistent product quality.
Contact Us
Email: [email protected]; Or fill out the contact form below.

 English
English 中文简体
中文简体 русский
русский Español
Español Français
Français