What Is the Use of Thin Wall Injection Molds?
Thin wall injection molds have become increasingly important in the manufacturing world, especially where lightweight and efficient plastic parts are required. These molds are designed to produce components with very thin walls, often less than 1 millimeter thick, which brings unique challenges and advantages to the molding process. One of the primary uses of thin wall injection molds is in the production of lightweight plastic parts for industries such as packaging, automotive, electronics, and consumer goods. By producing thin walls, manufacturers can significantly reduce the amount of plastic material used in each part. This cost savings and environmental benefits due to less raw material consumption and lower transportation weights. Thin wall parts are especially popular in packaging applications, where containers, lids, and trays require strength while weight.
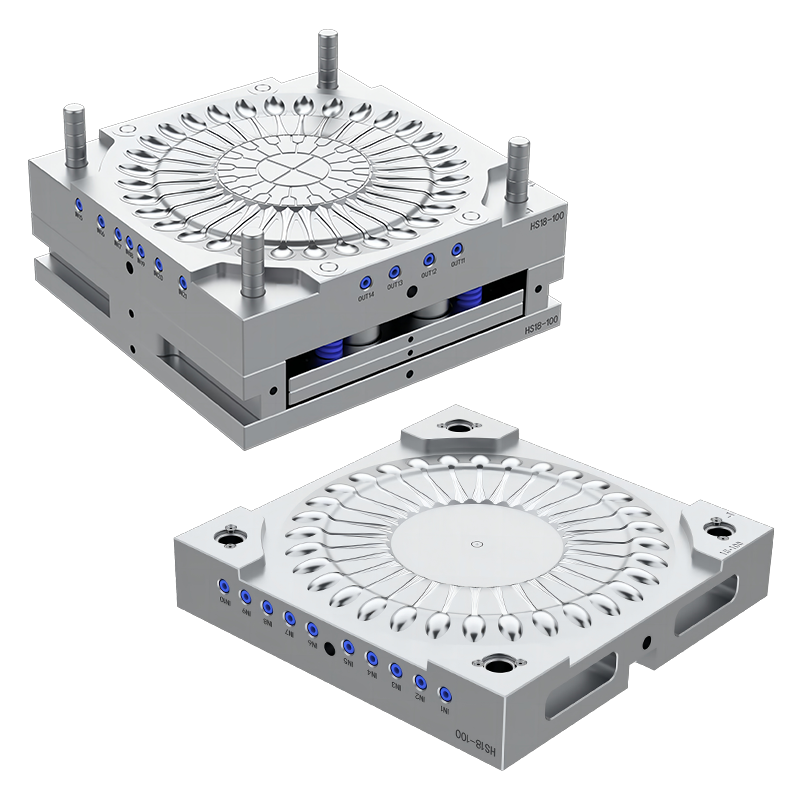
Another important aspect of thin wall injection molds is their ability to support high-speed production. Because thin walls cool faster than thick ones, cycle times are generally shorter, allowing manufacturers to produce more parts per hour. This high efficiency is vital for meeting large production demands and reducing manufacturing costs. However, the mold design and material selection must accommodate the faster cooling rates to avoid defects such as warping or incomplete filling.
Designing thin wall injection molds requires careful consideration of several factors. One major consideration is mold precision. Since the walls of the molded parts are thin, any variation or mismatch in mold halves can cause defects like flash or weak spots. The mold cavities must be machined with high accuracy, and the mold assembly should ensure tight alignment throughout production. To achieve this, mold makers often use hardened tool steels and advanced machining techniques such as CNC milling and EDM.
The material flow inside thin wall injection molds also poses challenges. Molten plastic must fill the cavity quickly before cooling and solidifying, which requires high injection speeds and pressures. The mold's gating system—the channels that direct molten plastic into the cavity—must be designed to minimize flow resistance and ensure balanced filling. Proper venting is equally critical, as trapped air can cause burns or voids in thin wall parts.
Cooling system design plays a crucial role in the use of thin wall injection molds. Since thin walls solidify rapidly, the mold's cooling channels must be optimized to maintain uniform temperature distribution. Uneven cooling can part distortion or internal stresses. Many molds employ conformal cooling channels, which follow the cavity contours closely and provide more efficient heat removal than traditional straight channels.
The ejection system in thin wall injection molds also requires attention. Thin parts are more prone to deformation or damage during ejection, so the ejector pins or plates must apply uniform and gentle force. In some cases, air-assisted or stripper plate ejection is used to avoid marking delicate surfaces or distorting the part.
Thin wall injection molds are also beneficial for creating parts with complex geometries that need to be lightweight. For example, automotive interior panels or electronic device housings often combine thin walls with intricate details. The precision and speed of these molds make them suitable for producing such parts while maintaining consistent quality.
Another area where thin wall injection molds find use is in producing medical devices and components. Many disposable medical parts, such as syringes or diagnostic device components, require thin walls for functionality and material efficiency. The molds used must meet strict standards for cleanliness and precision, often incorporating specialized surface finishes and materials.
Contact Us
Email: [email protected]; Or fill out the contact form below.

 English
English 中文简体
中文简体 русский
русский Español
Español Français
Français