What Are the Options for Food Container Mold?
Food container molds play a crucial role in the manufacturing process of various types of food storage products. These molds determine the shape, size, design, and functional properties of the containers, which directly influence their usability, durability, and appeal to consumers. Whether for household use, commercial food packaging, or industrial storage, selecting the appropriate food container mold is essential for producing quality containers that meet market needs and safety standards.
The choice of material for molds affects the durability, precision, and production efficiency of food containers. Common materials for food container molds include:
Steel Molds: Steel, particularly stainless steel or hardened tool steel, is the widely used mold material. It offers high strength, wear resistance, and dimensional stability, making it ideal for high-volume production. Steel molds can withstand the pressures and temperatures involved in molding processes and produce containers with consistent quality. They are also suitable for intricate designs.
Aluminum Molds: Aluminum molds are lighter and less expensive than steel molds, making them attractive for prototyping or low-volume production runs. Aluminum offers good thermal conductivity, which helps reduce cycle times in molding. However, aluminum molds may wear faster and are less suitable for very large production runs or detailed designs.
Composite Molds: These molds combine different materials, such as a steel frame with aluminum inserts, to balance cost and performance. Composite molds may be used to optimize production efficiency and extend mold life while controlling expenses.
Food container molds are designed according to the molding technique used and the container's intended function. The main types include:
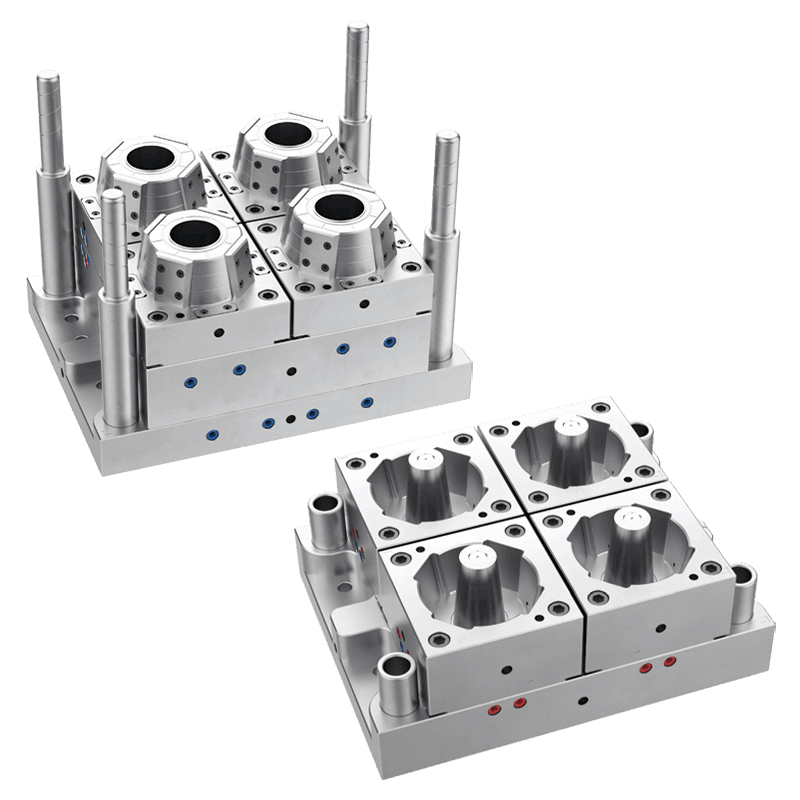
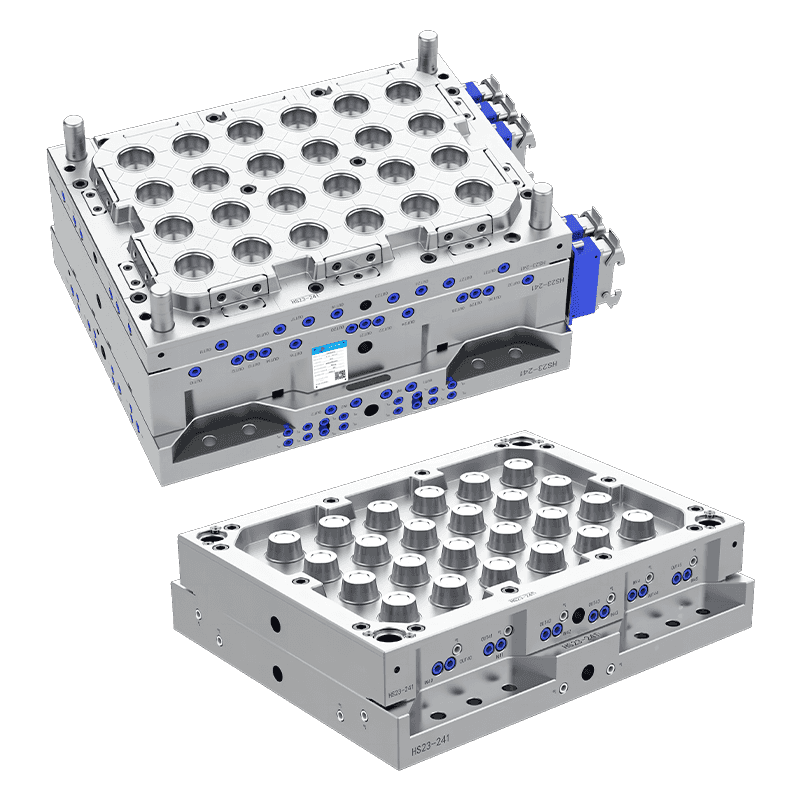
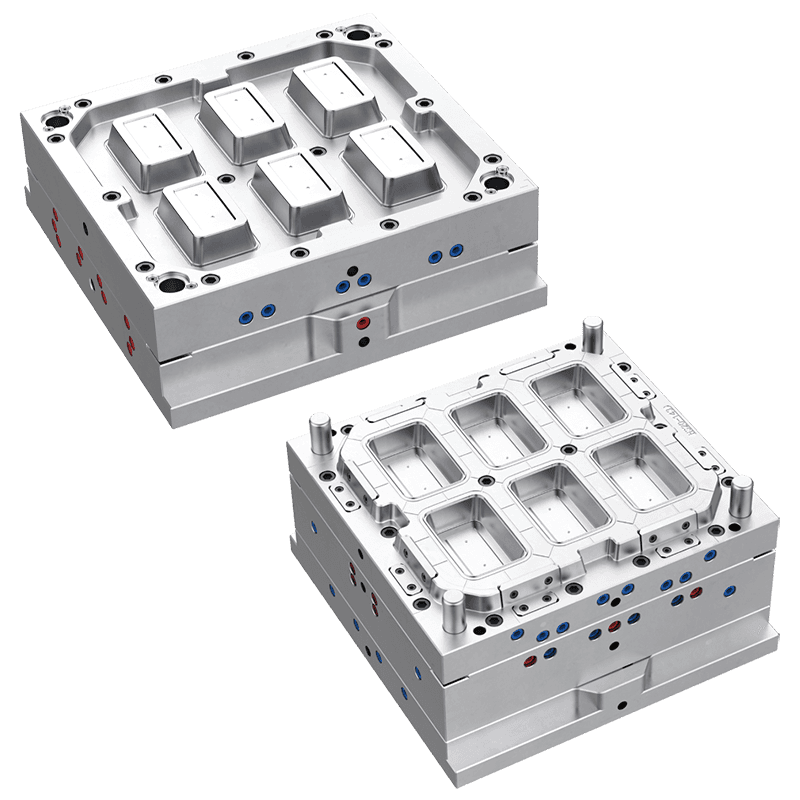
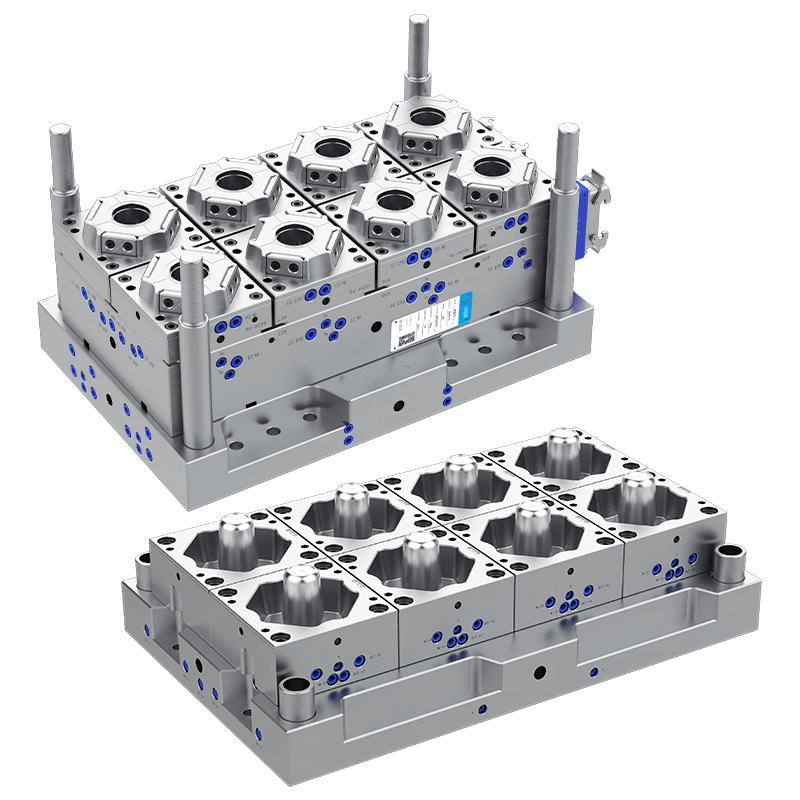
Injection Molds: Injection molding is commonly used for rigid plastic food containers. Molten plastic is injected into the mold cavity, cooled, and ejected as a solid container. Injection molds can produce complex shapes with high precision and surface finishes. They are suitable for producing containers like lunch boxes, deli containers, and stackable food storage boxes.
Blow Molds: Blow molding is ideal for hollow containers, such as bottles, jars, or large storage containers. The process involves inflating heated plastic inside a mold cavity, allowing the plastic to conform to the mold's shape. Blow molds are typically made for containers requiring uniform wall thickness and light weight.
Thermoforming Molds: Thermoforming involves heating plastic sheets and then forming them over molds using vacuum or pressure. This process is common for making food trays, clamshell packaging, and disposable containers. Thermoforming molds are usually simpler and less expensive than injection or blow molds.
Compression Molds: Compression molding is less common for food containers but may be used for certain materials like silicone or rubber-based containers. It involves pressing the molding material into the mold cavity under heat and pressure.
Mold design significantly affects the usability and market appeal of food containers. Options for customization include:
Shape and Size: Molds can be designed to create containers of various shapes—rectangular, square, round, or custom forms—to suit specific storage needs or branding preferences. Size customization allows for single-serving containers or large-capacity storage options.
Compartments and Dividers: Some food containers require multiple compartments for separating different food items. Molds can incorporate dividers and sections, which are common in lunch boxes or meal prep containers.
Lid Integration: Many food containers come with matching lids for sealing and protection. Mold options include creating containers and lids in the same mold set or producing them separately to optimize production.
Surface Texture and Decoration: Molds can impart different textures, such as matte, glossy, or patterned surfaces, affecting the container's appearance and grip. Additionally, branding elements like logos or labels can be integrated into the mold design.
Contact Us
Email: [email protected]; Or fill out the contact form below.

 English
English 中文简体
中文简体 русский
русский Español
Español Français
Français