Thin Wall Injection Molds: Characteristics and How to Choose
Thin wall injection molds are specialized tools used in the manufacturing of lightweight, high-precision plastic parts. They are widely applied in industries such as packaging, automotive, electronics, and consumer products. These molds are designed to produce parts with thin walls, which reduce material usage, lower production costs, and improve product efficiency.

Importance of Thin Wall Injection Molds
Thin wall injection molds are important because they allow manufacturers to produce lightweight plastic components without compromising strength or performance. The thin wall design reduces material consumption, making the production process more cost-effective and environmentally friendly. Additionally, thin wall injection molding enables faster cooling and cycle times, increasing production efficiency. Properly designed molds ensure consistent product quality, reduce defects, and improve the performance of the final parts, making them essential in high-volume manufacturing environments.
Key Characteristics of Thin Wall Injection Molds
Several characteristics define the performance and suitability of thin wall injection molds:
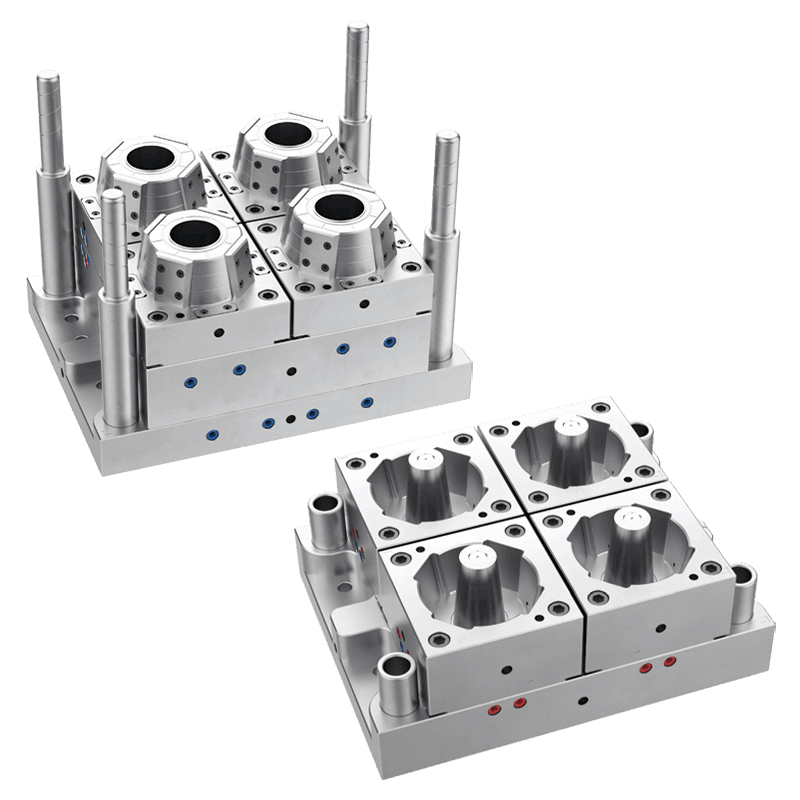
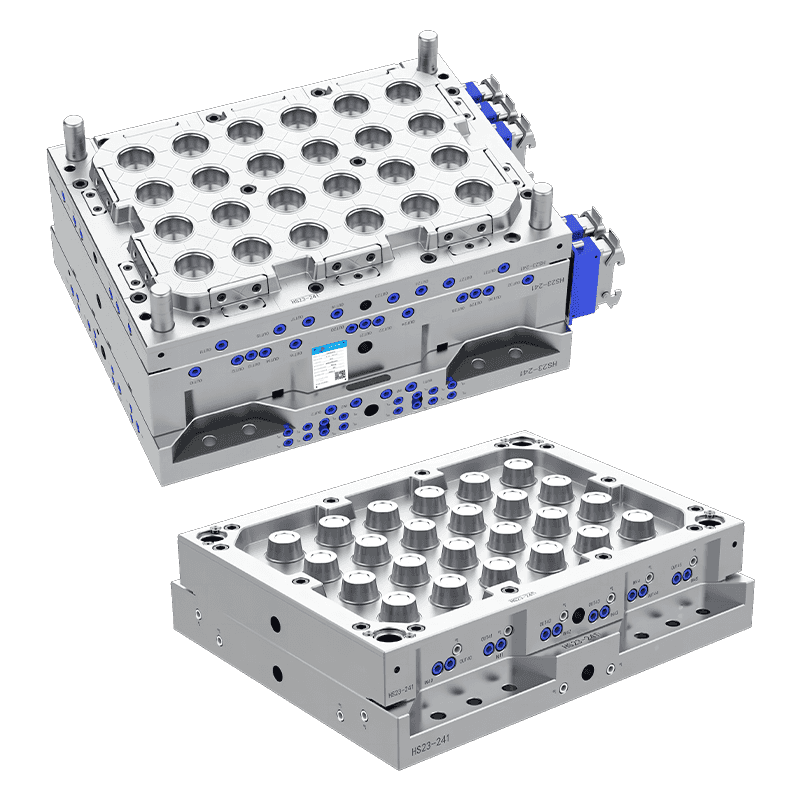
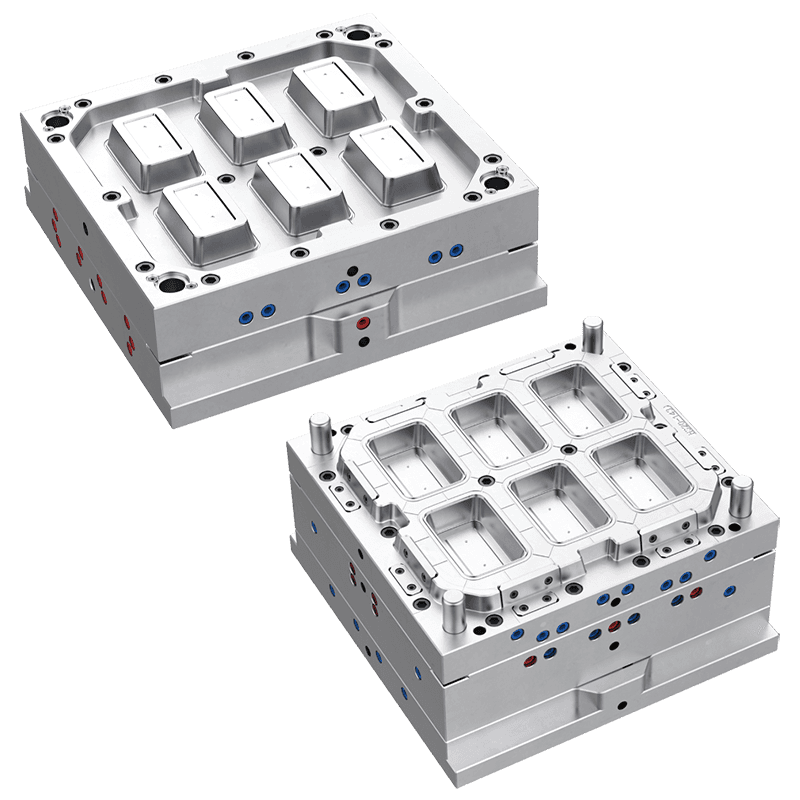
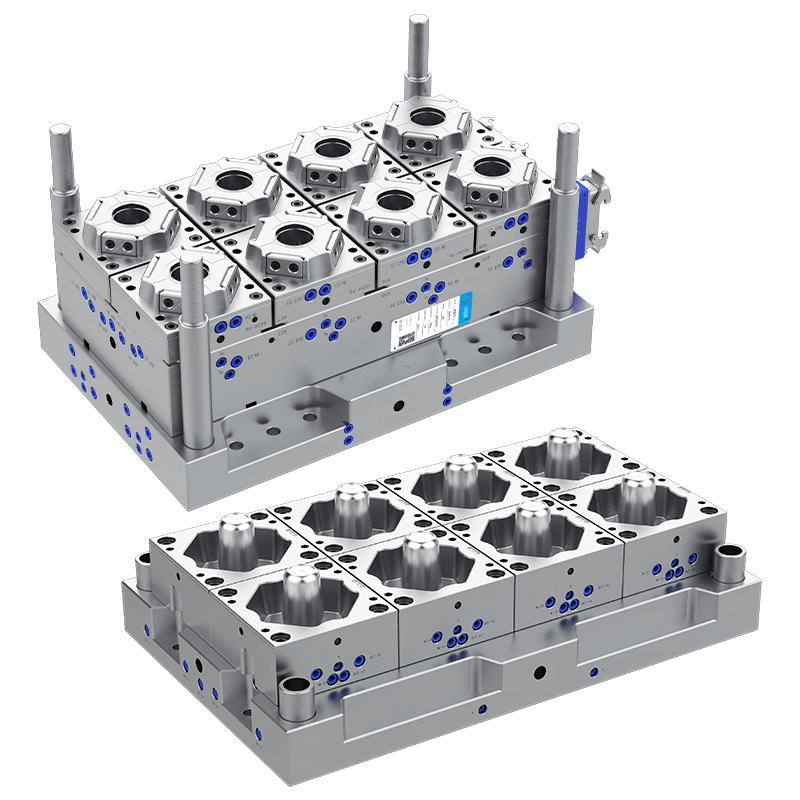
1. Material Quality and Mold Base
The mold base and components are typically made from high-quality steel, such as P20, H13, or stainless steel. P20 steel is commonly used for general-purpose molds due to its toughness and wear resistance. H13 steel provides heat resistance, making it suitable for high-speed production and high-temperature applications. Stainless steel offers corrosion resistance for molds exposed to humid or chemical environments. High-quality mold materials ensure durability, precision, and long service life.
2. Wall Thickness Precision
Thin wall injection molds are designed to produce walls as thin as 0.3 mm to 2 mm, depending on the application. Maintaining uniform wall thickness is crucial for part strength, dimensional accuracy, and aesthetic quality. Advanced mold design and precise machining ensure consistent wall thickness, warping, sink marks, and deformation.
3. Cooling System Efficiency
An efficient cooling system is essential for thin wall molds due to the reduced material thickness. Rapid cooling channels help maintain uniform temperature, reduce cycle time, and prevent warping or residual stress in the molded parts. Optimized cooling ensures consistent part quality and improves production efficiency.
4. Ejection System Design
Thin wall parts can be delicate, requiring precise ejection mechanisms to avoid deformation or damage. Ejection pins, plates, or air-assisted systems help remove parts smoothly from the mold. Proper ejection design ensures minimal handling issues and maintains the quality of finished components.
5. Mold Cavity Configuration
Thin wall molds may feature single-cavity, multi-cavity, or family molds depending on production volume and part design. Multi-cavity molds allow high-volume production with uniform parts in each cycle. Family molds enable multiple types or sizes of parts to be produced simultaneously, optimizing efficiency.
6. Surface Finish and Texture
The surface finish of the mold directly impacts the appearance of thin wall parts. Polished molds produce smooth, glossy surfaces, while textured molds provide matte finishes or functional textures. Proper surface finishing ensures visual appeal, functional performance, and ease of demolding.
How to Choose a Thin Wall Injection Mold
Selecting the right thin wall injection mold involves considering several factors:
Production Volume: Multi-cavity molds are ideal for high-volume production, while single-cavity molds suit smaller batches or prototypes.
Material Type: Consider the type of plastic used, such as polypropylene, polystyrene, or ABS, and ensure the mold material and design are compatible.
Wall Thickness Requirements: Choose molds capable of producing consistent thin walls according to part specifications.
Cooling Efficiency: Select molds with optimized cooling channels to reduce cycle time and prevent defects.
Ejection Design: Ensure the mold has a precise ejection system to prevent deformation of delicate parts.
Surface Finish: Determine the desired appearance and texture of the final product and select a mold with the appropriate finish.
Maintenance and Longevity: Choose molds made from durable materials that allow easy maintenance and long-term use.
Applications of Thin Wall Injection Molds
Thin wall injection molds are widely used in industries requiring lightweight, precise plastic parts:
Packaging Industry: Production of thin-walled containers, lids, trays, and disposable cups.
Automotive Industry: Lightweight components such as interior panels, clips, and housings.
Electronics Industry: Casings, connectors, and protective covers for devices.
Consumer Products: Household items, toys, and kitchenware requiring thin, durable plastic parts.
Contact Us
Email: [email protected]; Or fill out the contact form below.

 English
English 中文简体
中文简体 русский
русский Español
Español Français
Français