Thin Wall Food Container Mould: What Are Three Common Types?
Thin wall food container moulds are widely used in the manufacturing of disposable and reusable food packaging. These moulds are designed to produce containers with uniform thickness, adequate strength, and consistent shape, suitable for various food storage and serving purposes. Different mould types offer distinct advantages depending on the production method, material type, and desired product characteristics.
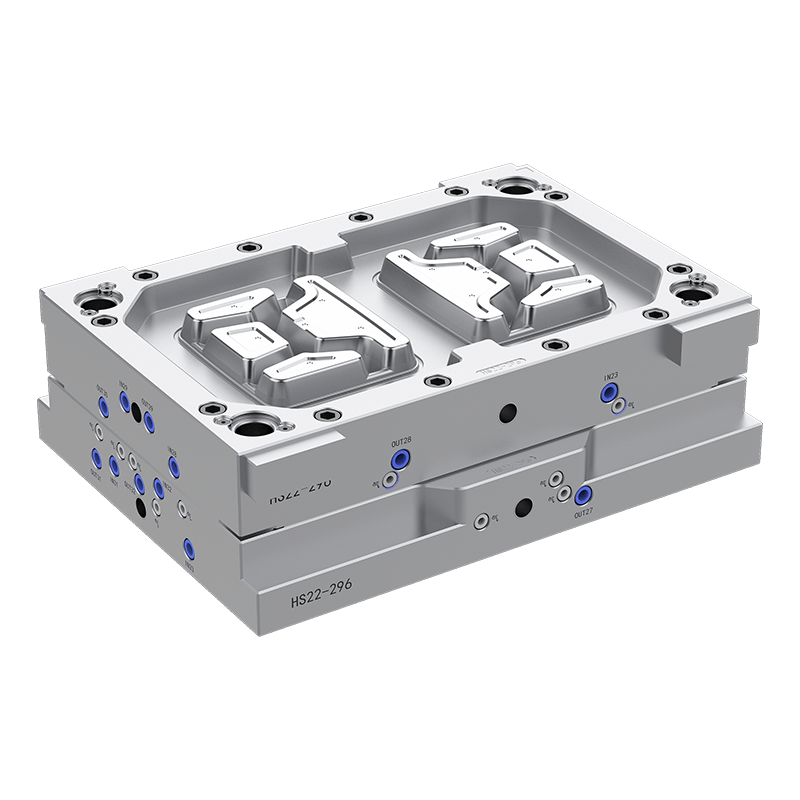
Injection Moulds for Thin Wall Food Containers: Precision and Efficiency
Injection moulds are among the most commonly used types for producing thin wall food containers. These moulds operate by injecting molten plastic into a mould cavity under high pressure. The plastic quickly fills the cavity, forming the desired container shape. The process is widely used for producing polypropylene (PP), polyethylene (PE), or polystyrene (PS) containers.
Key Features of Injection Moulds
High Precision: Injection moulds allow for precise control over wall thickness and shape. This ensures uniformity in each container and reduces material waste.
Fast Production Rate: The cycle time for injection moulding is relatively short, making it suitable for high-volume production. This efficiency is essential for manufacturers meeting large-scale market demands.
Design Flexibility: These moulds can produce containers of various shapes, including square, rectangular, round, or custom designs. Decorative textures and embossed patterns can also be incorporated into the mould.
Applications
Injection moulds are often used to produce food containers for ready-to-eat meals, takeaway boxes, and storage containers. The process ensures that containers are durable enough for handling and stacking while maintaining thin walls to reduce material consumption. These moulds are suitable for both disposable and reusable containers, depending on the material used.
Thermoforming Moulds for Thin Wall Food Containers: Versatility and Adaptability
Thermoforming is another common method for producing thin wall food containers. In this process, a plastic sheet is heated until pliable and then formed into a container shape using a mould. Thermoforming is particularly effective for creating shallow or medium-depth containers.
Key Features of Thermoforming Moulds
Adaptability: Thermoforming moulds can accommodate a variety of container shapes and sizes. This allows manufacturers to produce different container types using the same machine with minimal adjustment.
Surface Detail: The mould can include textures or branding elements, enhancing the visual appeal and tactile feel of the container.
Material Efficiency: Because thermoforming uses a sheet of plastic, it allows for better control of material usage and reduces waste compared with other methods.
Applications
Thermoformed thin wall containers are widely used for bakery trays, fruit or vegetable trays, and meal prep containers. This method is also suitable for packaging with compartments, as the mould can be designed to form multiple sections in a single container. Thermoforming is often chosen for food packaging where visual presentation is important, such as clear lids or display trays.
Blow Moulds for Thin Wall Food Containers: Lightweight and Hollow Shapes
Blow moulding is a less common but useful technique for producing thin wall food containers, particularly when the container needs to be hollow or have a significant internal volume. In this method, molten plastic is extruded into a tube, known as a parison, which is then inflated inside a mould to form the desired shape.
Key Features of Blow Moulds
Hollow Structure: Blow moulding is ideal for creating containers that require a hollow interior, such as bottles or jars. This makes it suitable for liquids, sauces, or condiments.
Lightweight Design: Thin wall containers produced through blow moulding can be lightweight yet strong enough to hold their contents securely.
Consistent Thickness: The process allows for relatively uniform wall thickness, which is important for stacking and handling.
Applications
Blow moulded thin wall containers are commonly used for food products that need airtight sealing or liquid storage. Examples include juice bottles, sauce containers, and some condiment packaging. The hollow structure enables easy filling and reduces the amount of material needed while maintaining sufficient strength for transportation.
Considerations for Choosing the Appropriate Thin Wall Food Container Mould
Selecting the right thin wall food container mould involves evaluating factors such as production volume, material type, container design, and end-use requirements. Each mould type offers distinct advantages and limitations that influence its suitability for specific applications.
Production Volume and Efficiency:
Injection moulds are often preferred for high-volume production due to their fast cycle times, while thermoforming is suitable for moderate volumes with flexible design options. Blow moulding is effective for hollow containers but may be slower or less precise for complex shapes.
Material Compatibility:
The type of plastic used affects the choice of mould. Injection moulds work well with PP, PE, and PS, thermoforming suits PET and HIPS sheets, and blow moulding is typically used for PP or HDPE bottles. Material properties influence wall thickness, durability, and thermal resistance.
Design Requirements:
Considerations include container shape, size, wall thickness, and the need for compartments or textured surfaces. Injection moulds allow for highly detailed and uniform designs, thermoforming provides adaptability for trays and shallow containers, and blow moulding is ideal for hollow or cylindrical shapes.
Cost and Maintenance:
Initial investment and maintenance requirements vary. Injection and blow moulds may have higher upfront costs but provide long-term efficiency for large-scale production. Thermoforming moulds are generally more cost-effective for smaller runs and design variations. Regular maintenance ensures consistent quality and prolongs the life of the mould.
Contact Us
Email: [email protected]; Or fill out the contact form below.

 English
English 中文简体
中文简体 русский
русский Español
Español Français
Français