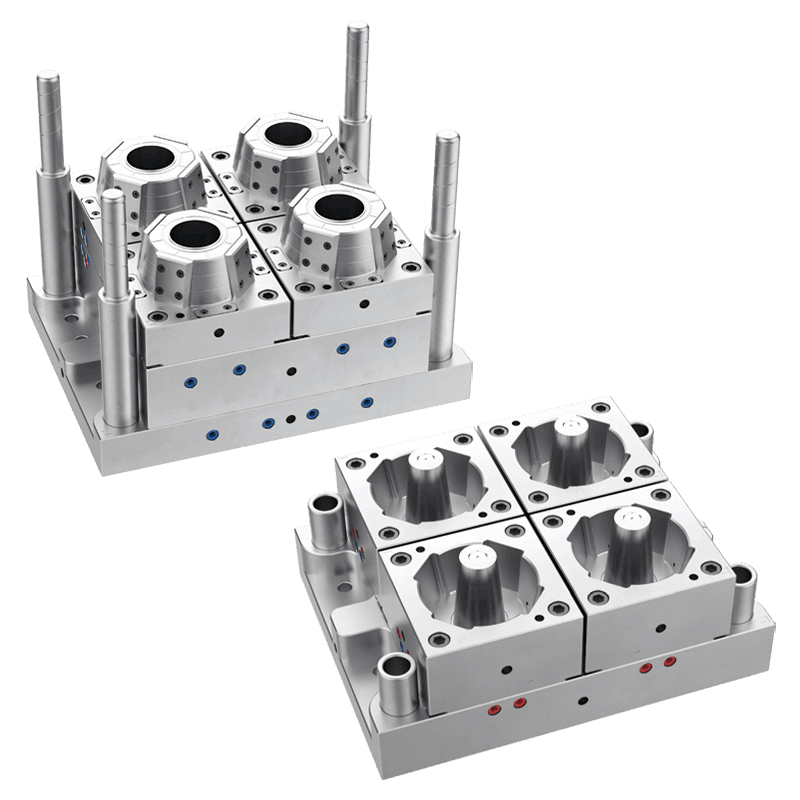
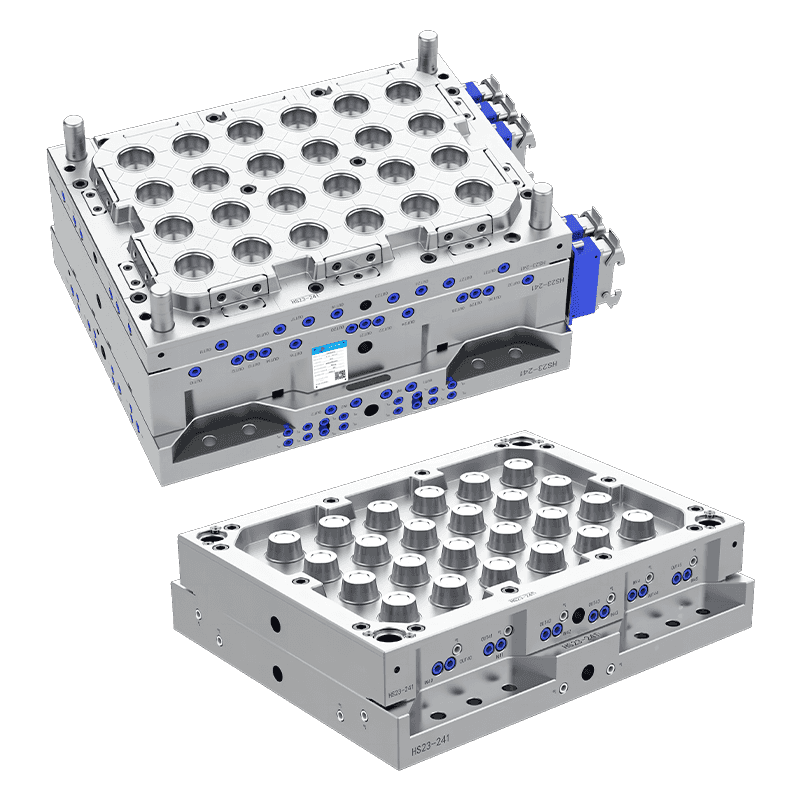
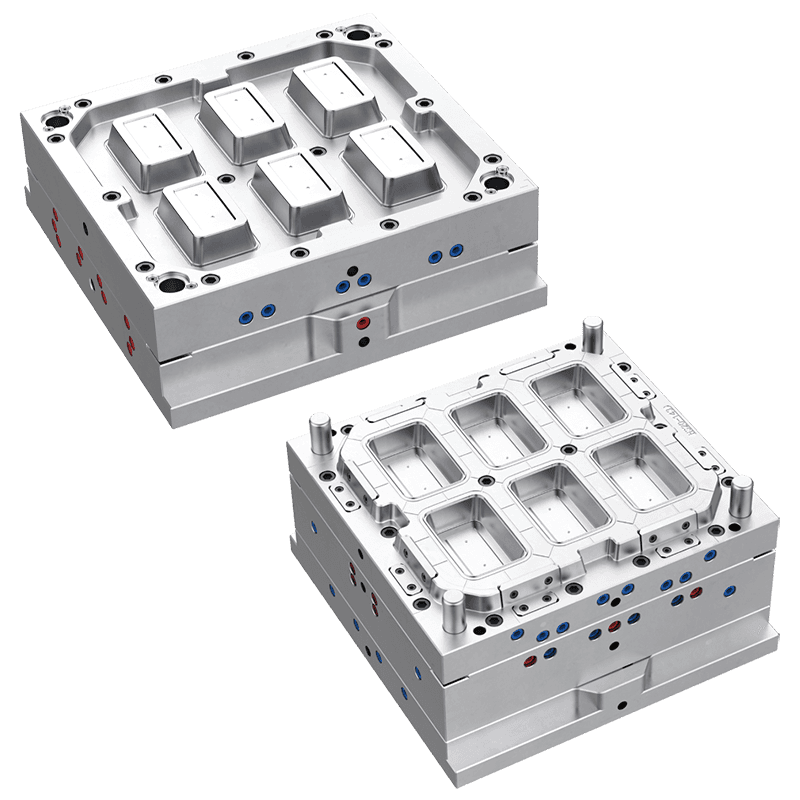
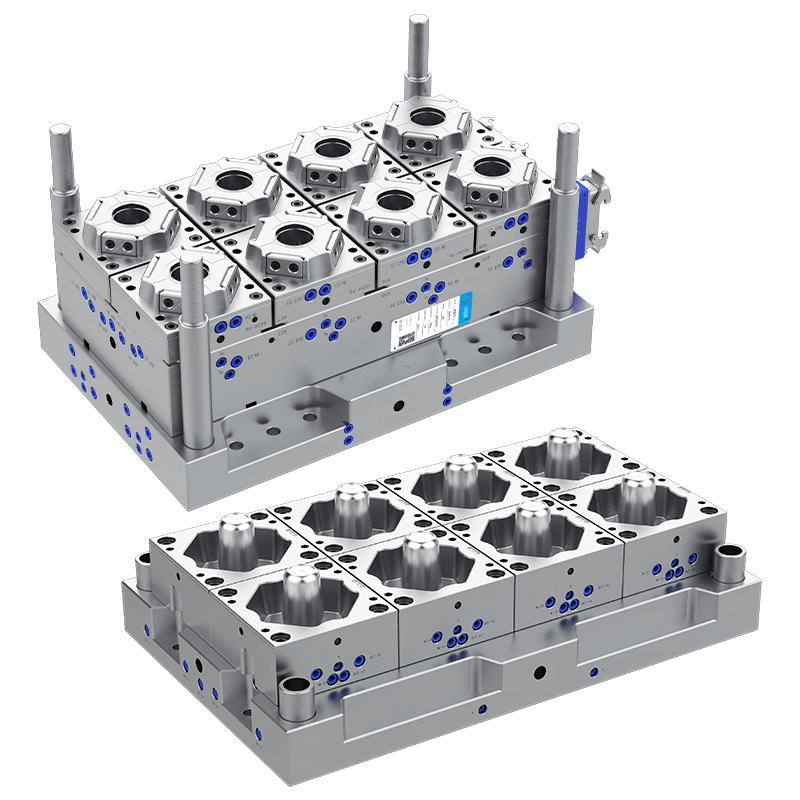
The Specifications and Dimensions of Thin Wall Food Container Moulds
A Thin Wall Food Container Mould is a specialized mould used to manufacture plastic food containers with thin walls. These containers are commonly used in packaging a wide variety of food products, such as takeout meals, salads, and desserts. Thin-walled containers are advantageous because they use less material, reducing both weight and cost while still offering the required strength and durability.

These moulds are typically made of high-quality steel or aluminum to ensure durability and heat resistance during the injection moulding process. The design and dimensions of these moulds are carefully engineered to produce containers that meet strict regulatory standards for food safety and functionality.
Key Specifications of Thin Wall Food Container Moulds
The specifications of a Thin Wall Food Container Mould are critical to its performance and the quality of the containers it produces. Some of the key specifications include:
a. Mould Material
The material of the mould is one of the important specifications. Thin Wall Food Container Moulds are typically made from high-strength steel or aluminum alloys. These materials are chosen for their ability to withstand high temperatures and pressures during the injection moulding process. Steel is often preferred for its durability and resistance to wear, while aluminum is valued for its lighter weight and thermal conductivity.
The choice of material affects the overall cost of the mould, its lifespan, and the speed at which the mould can produce containers. High-quality mould materials ensure that the mould can handle repeated use without degradation, which is crucial for high-volume production.
b. Injection System
The injection system in a Thin Wall Food Container Mould determines how the molten plastic is injected into the mould cavity. This system must be designed to deliver the right amount of plastic evenly throughout the mould to ensure uniform container walls. The injection system can include a hot runner or a cold runner system, depending on the design and production requirements.
A hot runner system helps reduce material waste by keeping the plastic melted while it flows into the cavity, whereas a cold runner system uses a more traditional method of injecting plastic, which can result in more waste. The choice of the injection system impacts both the cost and the efficiency of the production process.
c. Cooling System
Cooling is another vital aspect of the Thin Wall Food Container Mould design. An efficient cooling system is necessary to solidify the molten plastic quickly, improving cycle times and reducing energy consumption. The cooling system typically involves a series of channels embedded in the mould, through which a coolant (often water) flows to absorb heat from the mould.
The cooling system needs to be precisely designed to ensure that the plastic solidifies uniformly throughout the mould. If the cooling is not even, it could result in defects in the final product, such as warping or uneven wall thickness.
d. Mould Cavity Design
The design of the mould cavity is fundamental to the shape, size, and thickness of the food containers produced. Thin Wall Food Container Moulds are designed with a highly accurate cavity shape that matches the desired dimensions of the final product. Precision is key to ensure that the containers are uniform in size, with smooth walls and consistent thickness.
Additionally, the mould cavity design also needs to consider the specific features of the food container, such as handles, lids, or vents, which require additional moulding techniques.
Contact Us
Email: [email protected]; Or fill out the contact form below.

 English
English 中文简体
中文简体 русский
русский Español
Español Français
Français