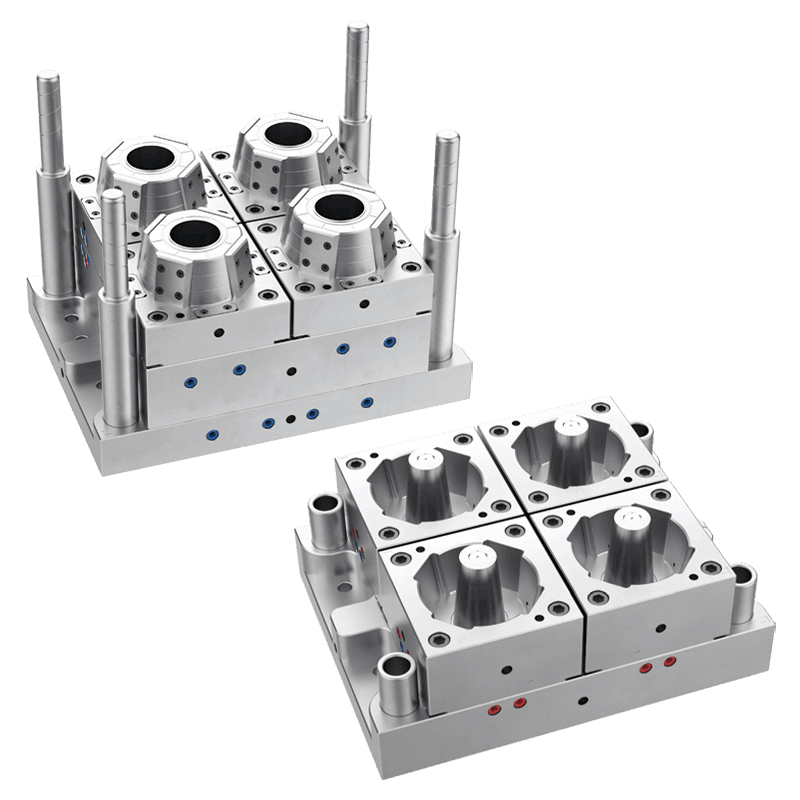
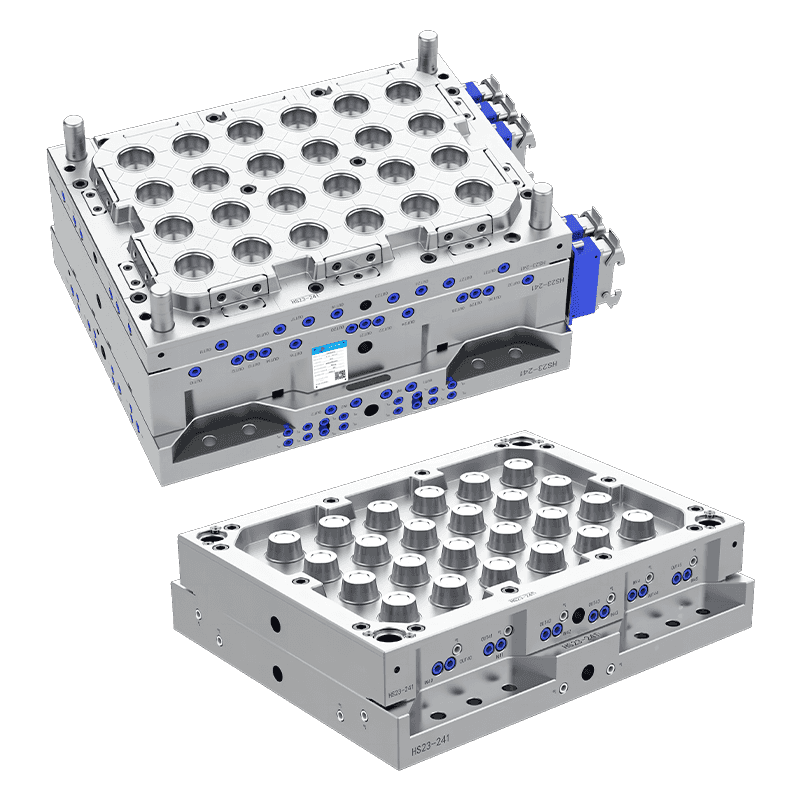
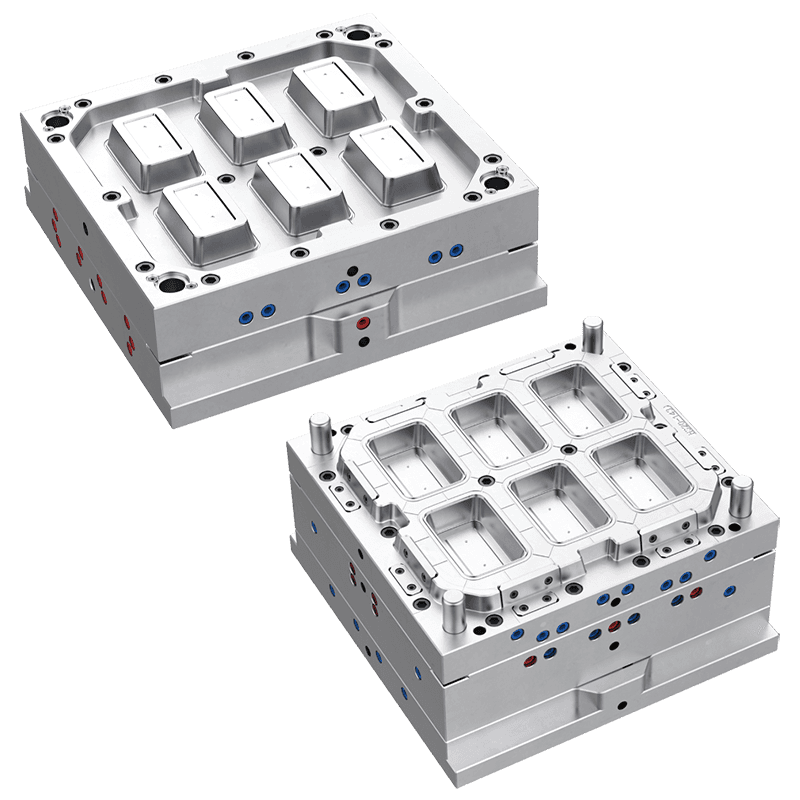
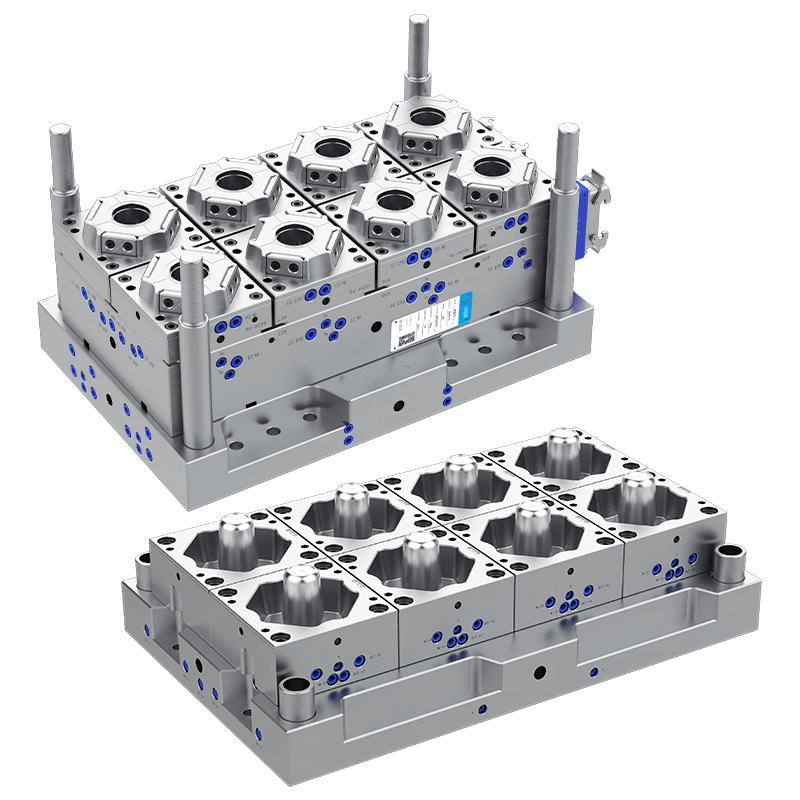
What are the common uses of a Plastic Food Container Mould?
The modern food distribution system relies heavily on standardized, hygienic, and cost-effective packaging. Central to the production of this packaging is the plastic food container mould, a precision tool used in injection molding machines to mass-produce containers from various polymer materials. This mould is not a single product but a custom-engineered cavity that defines the shape, texture, and functionality of the final container. Its applications are extensive, directly corresponding to the diverse needs of food storage, transportation, and presentation across multiple sectors. The common uses of these moulds can be categorized by the type of container they produce and the specific demands of the food products they are designed to hold.
Part 1: Production of Short-Term Storage and Takeaway Containers
This represents one of the most visible and high-volume applications for plastic food container moulds. These containers are designed for single-use or short-term use, prioritizing functionality, low cost, and stackability.
1.1. Disposable Clamshell Containers
Moulds for clamshell containers produce ubiquitous items used by restaurants, cafes, and grocery stores. These containers feature a hinged lid that snaps shut, securing items like salads, burgers, pastries, and sliced fruits. The mould must create a precise hinge mechanism that withstands repeated opening and closing without breaking, and often includes features for venting to prevent moisture buildup.
1.2. Single-Compartment Takeaway Trays
For hot foods, moulds are designed to create trays from heat-resistant plastics like polypropylene (PP) or crystallized polyethylene terephthalate (CPET). These trays are used for ready meals, Chinese takeaway, and airport food services. The moulds ensure consistent wall thickness for even heat distribution in microwaves and often include reinforced rims for structural integrity when stacked.
1.3. Deli and Bakery Packaging
Specific moulds are engineered for clear, thin-walled containers used in deli counters and bakeries. These containers allow for product visibility and are designed to be lightweight, material cost. The moulds for these applications must achieve high-clarity finishes on the plastic to make the food items visually appealing.
Part 2: Manufacturing of Durable, Reusable Food Containers
At the consumer level, moulds are used to produce robust containers designed for repeated use in home and commercial kitchens. Durability and sealing capability are paramount here.
2.1. Airtight Storage Sets
Moulds for household storage containers create a range of interlocking, stackable sizes, often sold as sets. The critical feature is the lid seal. The mould must produce a lid with an integrated gasket or a precisely engineered groove that forms an airtight seal with the container base, preserving food freshness and preventing spills. Brands like Tupperware and Rubbermaid rely on highly precise moulds to achieve their signature seals.
2.2. Commercial Food Storage and Transport
In restaurants, catering services, and food processing plants, large, heavy-duty containers are required. Moulds for these produce bins and pails, often with capacities of several liters. These containers are designed to withstand rough handling, and their moulds often include features for reinforced handles, thick walls, and compatibility with standard racking systems.
Part 3: Creating Specialized Packaging for Specific Food Types
Certain food products have unique packaging requirements that demand specialized mould designs to address issues of preservation, presentation, or portion control.
3.1. Berry and Produce Boxes
The plastic containers for berries, cherry tomatoes, and mushrooms are a distinct category. Their moulds create a ventilated design, with numerous small holes in the body to allow for air circulation, which is crucial for extending the shelf life of fresh produce. These moulds also often include a recessed area for a branded label or price sticker.
3.2. Dairy and Margarine Tubs
Moulds for dairy products like yogurt, sour cream, and margarine produce shallow, wide-mouthed tubs. The design prioritizes easy scooping and a stable base. The mould must create a container with a smooth inner surface for easy cleaning and a lip that allows for secure foil or plastic seal application by filling machines.
3.3. Bottles and Jars for Condiments
While blow moulding is common for bottles, injection moulding is used to create wide-mouth jars for sauces, dressings, and condiments, as well as the caps for a vast range of bottles. These moulds must produce threads that are precise and consistent to ensure a leak-proof seal when the cap is applied with a specific torque on automated filling lines.
Contact Us
Email: [email protected]; Or fill out the contact form below.

 English
English 中文简体
中文简体 русский
русский Español
Español Français
Français